NASA has raised alarms over a significant anomaly currently developing across the Earth’s surface. Scientists are tracking the South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA), a vast area where the magnetic field has notably weakened. This peculiar phenomenon not only raises questions about geomagnetic dynamics but also poses serious threats to our space technology. The origins of this anomaly are rooted deep within our planet, linked to complex processes and shifts occurring in Earth’s interior. Understanding this evolving situation is crucial, as it impacts the safety of satellites and prompts scientists to explore enigmatic forces shaping our planet.
The South Atlantic Anomaly: A Geomagnetic Enigma
The South Atlantic Anomaly, a sizable region of weakened magnetic intensity, stretches over South America and parts of the South Atlantic Ocean. Unlike other regions with robust magnetic fields, the SAA presents a significant vulnerability, acting as a gateway for high-energy solar particles to penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere. For those uninitiated in geophysics, this sight may seem just another aspect of Earth’s complexity, but the repercussions are tangible and far-reaching.
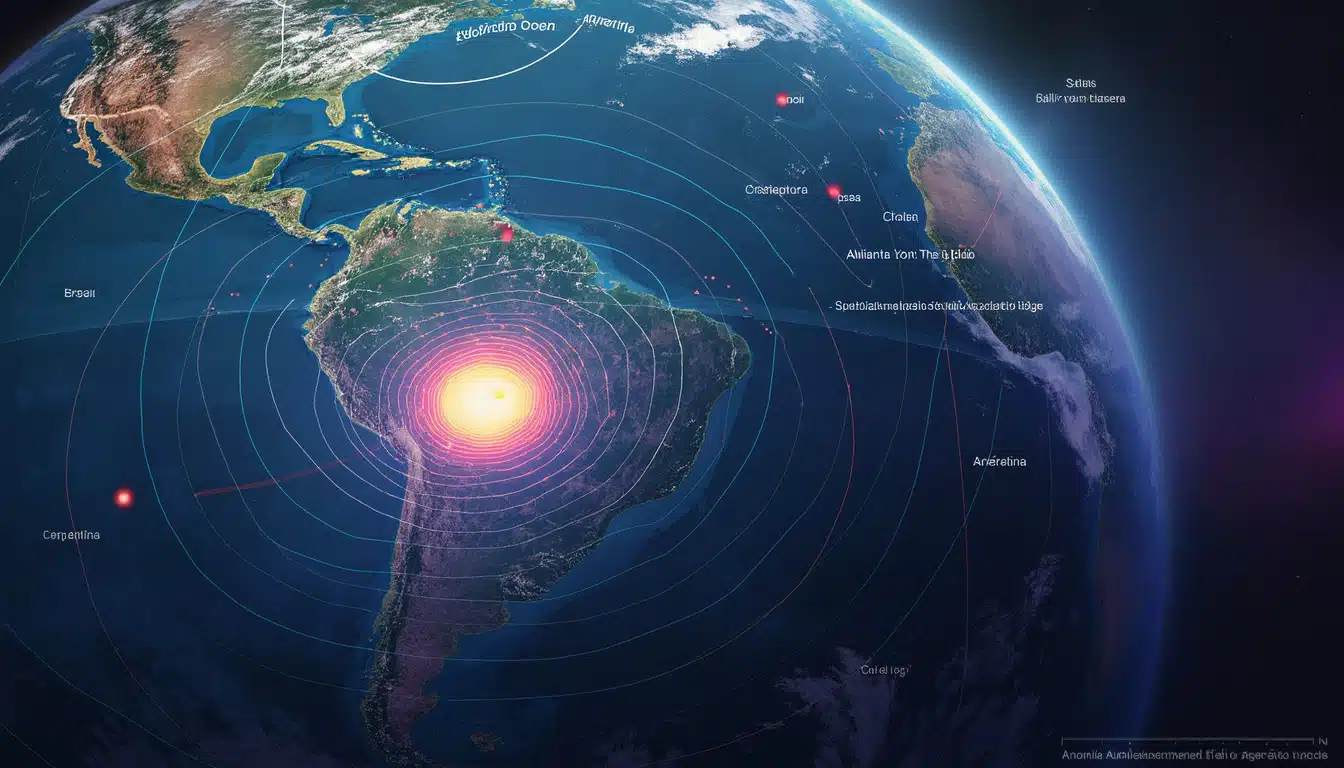
Understanding the Origins of the Anomaly
The SAA’s origins are deeply intertwined with the geodynamo, a complex process generated by the movement of molten iron and nickel within Earth’s outer core. This remarkable mechanism produces the magnetic field that envelops our planet, shielding it from solar radiation. However, not all regions exhibit uniform magnetic intensity, leading to intriguing phenomena like the SAA.
Two major factors contribute to the anomaly’s formation. The tilt of Earth’s magnetic axis relative to its rotational axis creates irregularities. Additionally, a unique geological structure beneath the African continent known as the African Large Low Shear Velocity Province disrupts the magnetic field generation process in this area. This irregular feature, located approximately 1,800 miles beneath the earth, mirrors how complex the planet’s interior processes can be.
This anomaly has serious implications, especially for various space missions. Satellites that traverse the SAA get exposed to high levels of energetic protons, which can lead to single event upsets (SEUs). Such events can cause temporary malfunctions or data corruption, jeopardizing mission objectives and increasing operational costs.
Threats to Satellites and Space Missions
NASA is acutely aware of the disruptions posed by the SAA on space technologies. As the anomaly continues to shift, it presents increasing risks for satellites. Operators often respond by employing precautionary measures, including downgrading equipment during traversals through the SAA to minimize potential harm. Even the International Space Station, with its protective shielding, experiences glitches from time to time, impacting the data collection process and mission efficiency.
Recent data reveal that the SAA is not static; it has been drifting northwest and expanding its coverage area. More alarmingly, the anomaly is starting to split into two separate lobes, leading to an increase in zones where significant magnetic weakening occurs. This dynamic behavior complicates the predictive modeling surrounding its impacts.
The history of the SAA provides insight into how scientists can better anticipate future developments. Researchers are currently monitoring how the anomaly shifts and evolves using satellite data from various missions and ground-based measurements. This ongoing work helps in refining models essential for planning safe and efficient space missions, as well as in better understanding geomagnetic forces.
The Ties between the SAA and Earth’s Interior Dynamics
The connections between the South Atlantic Anomaly and Earth’s interior processes illuminate the planet’s complexity. Researchers believe that studying the SAA reveals not only insights into magnetic behavior but also broader geological dynamics. The interactions between geophysical processes can shape our understanding of Earth’s history and its potential future.
Implications for Future Space Missions
As scientific initiatives from major space organizations like Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Northrop Grumman become more ambitious, understanding the SAA’s impact is critical. Missions by Blue Origin and SpaceX are increasingly reliant on satellite technology and capable of being hindered by anomalies like the SAA. Space agencies need to incorporate the understanding of the SAA into their operational frameworks, ensuring that data integrity remains high while navigating through such challenging regions.
The anomaly raises concerns regarding not only current space missions but also our future scientific endeavors. Tracking the evolution of Earth’s magnetic field over time is vital for a comprehensive understanding of the forces at play inside our planet. For example, organizations like Astrobotic and Planet Labs that focus on planetary exploration should prioritize understanding the SAA’s impacts in their mission designs.
Development of globally interconnected satellite systems is key to tackling upcoming challenges posed by anomalies like the SAA. Through collaboration, experts can aggregate data and improve technologies for high-risk orbital operations. The implications of this anomaly necessitate a groundbreaking approach to space exploration and understanding how terrestrial phenomena interact with our innovative technologies.
Predicting the Evolution of the South Atlantic Anomaly
Understanding the trajectory and impact of the SAA involves sophisticated computational models and simulations. NASA combines satellite data with geophysical models to refine predictions about the SAA’s progression. The International Geomagnetic Reference Field (IGRF) serves as a crucial tool for tracking the magnetic field’s evolution, akin to weather forecasting but spanning much longer timeframes.
The Role of Historical Geological Data
Historical geological records suggest that phenomena akin to the SAA have emerged throughout Earth’s history. A study dating back to 2020 posits that similar magnetic anomalies existed up to 11 million years ago. Although alarming, the current behavior of the SAA does not signal an imminent magnetic pole reversal, which is a rare event unfolding over hundreds of thousands of years. Nevertheless, studying the anomaly remains paramount for the safety of existing satellites and for an enhanced understanding of our planet’s inner workings.
Navigating through an age of rapid technological advancement compels scientists to remain vigilant in their analyses. The complex intricacies of the SAA require concerted effort, as changes in the anomaly can result in significant shifts in how we interact with space technologies. Agencies like NASA are committed to ongoing research and adaptability, enabling the scientific community to mitigate risks effectively.
Collaborative Research and Future Insights
Continuing to monitor the SAA, various organizations work together, sharing perspectives and data to foster a deeper understanding of the anomaly. Collaborations include not only NASA but also private companies and academic institutions, forming a united front against the challenges imposed by this unusual phenomenon. As our grasp of the SAA deepens, it will certainly influence future technological and scientific pursuits.
Keeping an Eye on the South Atlantic Anomaly
As the South Atlantic Anomaly continues to evolve, the implications for terrestrial and space technologies remain a subject of serious consideration. Monitoring this phenomenon will require cooperation among various stakeholders, bolstering our collective understanding and capabilities. As scientists decode this magnetic enigma, they unlock potential revelations about Earth’s magnetic dynamics and their intricate correlation with our technological advancements.
Future Developments and Recommendations
Understanding the trajectory of Earth’s magnetic fields requires an interdisciplinary approach. Insights from geomorphology, geophysics, and aerospace engineering can collectively contribute to improved predictive tools for space missions. As the SAA grows increasingly complex, developing tailored satellite technology equipped to withstand anomalies alongside comprehensive monitoring systems becomes essential.
In the long run, investing in research infrastructure becomes vital for those aspiring to explore beyond Earth. The interplay between the SAA and human innovation encapsulates a delicate balance between curiosity and caution as we endeavor deeper into space. Our understanding of what lies beneath the surface informs our ambitious explorative nature, shaping the future trajectory of space enterprises.

Engagement from public and governmental sectors, as well as sustained research efforts, will be paramount for future advancements aimed at navigating the ever-evolving complexities of space and its impact on Earth. The investigation of the SAA will remain a vital research area in safeguarding our satellites and enhancing our understanding of Earth’s magnetic dynamics.




Leave a Reply