The recent launch of an experimental reentry capsule by a German startup has highlighted the challenges of space missions. The capsule, named PHOENIX 1, was intended to safely return to Earth after a mission aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. However, due to unexpected changes in its flight path, the capsule splashed down far from its designated recovery area, resulting in the loss of critical data. This incident not only raises questions about the planning and execution of such missions but also underscores the unpredictability that comes with space explorations. Let’s delve deeper into the details of this mission, its implications for future launches, and what this means for the aerospace industry.
The Launch of PHOENIX 1
PHOENIX 1 was launched by ATMOS Space Cargo in a ride-share mission designed to lower costs for launching payloads into orbit. The Falcon 9 rocket, known for its reliability and reuse capabilities, lifted off at 8:48 p.m. ET on Monday, carrying various payloads including the experimental capsule. Initial plans had PHOENIX 1 following a specific trajectory that allowed for data collection during its anticipated return to Earth. With the mission including a South Korean military satellite and a weather satellite from a Boston firm, it positioned itself as an intriguing experiment in collaborative space exploration.

The Change in Flight Path
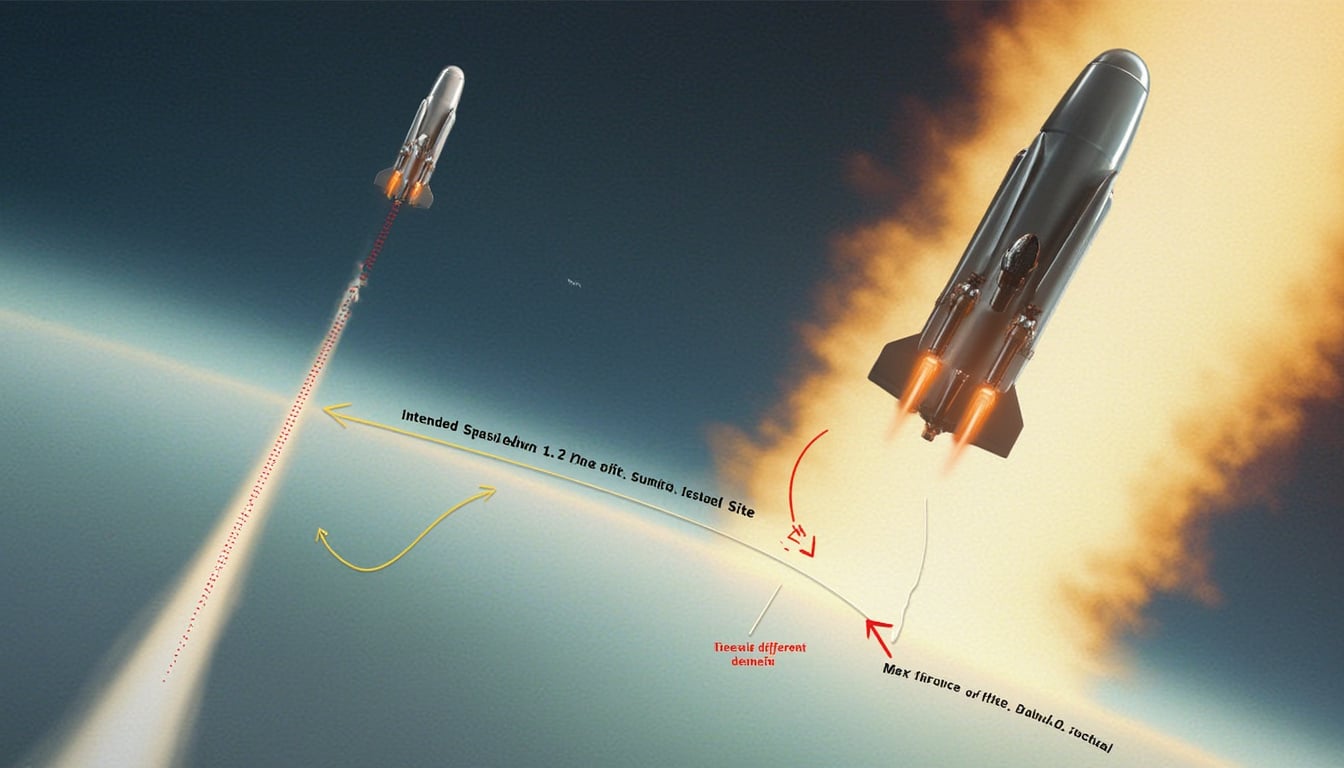
Complications emerged approximately five weeks before the scheduled launch when SpaceX notified ATMOS about a significant change in mission design. This alteration was necessary due to constraints connected to the primary South Korean satellite, ultimately impacting the flight path of PHOENIX 1. The capsule now had to adjust to a new return trajectory aimed at crossing over southern regions of the United States and South America instead of proceeding directly to the intended splashdown zone off the coast of La Réunion.
This adjustment illustrates a common challenge faced by aerospace companies: the need for flexibility and rapid response to unexpected operational changes. Such alterations not only complicate logistics but also increase the risks involved in the mission, leading companies to re-evaluate their strategies for data collection and recovery.
The Impact of Splashdown Misalignment
On reentry, PHOENIX 1 faced the intense conditions typical of such maneuvers. The mission’s objectives relied heavily on gauging the capsule’s heat shield performance, crucial for future designs targeting safe transport of research payloads. Unfortunately, the misalignment of the splashdown area—reported to be roughly 310 miles (500 km) off its intended location—prevented ATMOS from recovering the vessel.
The discrepancy meant the loss of potentially invaluable data crucial to the heat shield’s effectiveness during reentry. ATMOS officials expressed concerns about the impacts on their ongoing research and plans for future reusable spacecraft designs.
Data Recovery and Future Implications
Despite the setback, ATMOS managed to collect some data from four commercial payloads that were on board the capsule. Initial reports indicated success regarding the performance of the heat shield, suggesting that it withstood the intense temperatures of reentry. This positive data point offers a glimmer of hope for the development of future missions, but the lack of complete data still poses challenges.
The mishap underscores the critical nature of precise planning in launches, particularly with the growing competitive landscape in the aerospace sector, including players like NASA, Boeing, Blue Origin, and Lockheed Martin. As businesses like Rocket Lab, Virgin Galactic, and others continue to innovate and evolve, ensuring safety and reliability in designs will be paramount.
Lessons Learned from the PHOENIX 1 Mission
The unexpected challenges faced by the PHOENIX 1 mission provide several lessons not just for ATMOS but for the aerospace community at large. As the appetite for space exploration grows, and with numerous companies racing to establish their presence in the industry, the need for rigorous risk assessment becomes more pressing. The reentry mishap serves to remind the industry of the delicate balance between innovation and caution.
Exploring Risk Mitigation Strategies
One of the primary takeaways from the incident revolves around the importance of backend data collection strategies. Having a robust system for data analysis and recovery could define the future of space missions. As missions become increasingly collaborative—often involving multiple payloads like those in the PHOENIX 1 mission—maintaining clear communication and protocols among the involved parties is crucial.
Moreover, as noted by the CEO of ATMOS Space Cargo, Sebastian Klaus, the overall outcome of the mission could still be seen as a success. The data recovery from the commercial payloads and the heat shield’s confirmed performance suggest that existing technologies can still support the ambitions of space startups. This sentiment should inspire both optimism and caution in equally measure.
Future of Reentry Capsules
Looking ahead, the implications of this mission extend beyond ATMOS. Reentry capsules are fundamental to returning payloads safely—be it scientific research, equipment, or even astronauts. Companies such as the Aerospace Corp and Northrop Grumman are similarly invested in developing technologies that can withstand harsh space environments, reflecting a shared commitment to advancing these crucial aerospace endeavors.
International space agencies like the ESA (European Space Agency) are also observing lessons from such missions, continuously adapting their own technologies informed by both successes and failures. Understanding and learning from missions like PHOENIX 1 will foster an environment where innovations can thrive while maintaining safety as a priority.

Collaboration and Competition in Aerospace
The landscape of space exploration is rapidly evolving due to increased collaborations among private entities and governmental agencies. As competition heats up, innovation accelerates; each mission becomes a building block toward future success. Stakeholders, including lesser-known startups, have the opportunity to develop and refine their technologies, contributing to a more rigorous understanding of space travel.
Ultimately, linking the events surrounding the PHOENIX 1 mission to broader aerospace trends illustrates how both triumphs and failures are the catalysts for advancement in this field. The transition from theory into practical application will continue to shape the courses of missions for years to come.
| Key Elements of the PHOENIX 1 Mission | Description |
|---|---|
| Launch Date | 8:48 p.m. ET |
| Launch Vehicle | SpaceX Falcon 9 |
| Initial Splashdown Point | Targeted the Indian Ocean |
| Actual Splashdown | 310 miles off the Brazilian coast |
| Intended Data Collection | Heat shield performance during reentry |
| Payloads | Military and weather satellites plus PHOENIX 1 capsule |




Leave a Reply