A new chapter in American space exploration has begun to unfold under the leadership of Donald Trump, whose bold vision aims to elevate the United States to the forefront of interstellar endeavors. This article dives into the multifaceted aspects of Trump’s space policy, examining its impacts on key players like NASA, SpaceX, Blue Origin, and major aerospace contractors such as Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Northrop Grumman. The ambitions of Trump’s administration signal potential shifts in priorities and funding allocations that could reshape the trajectory of space exploration in the coming years. Exploring the intricate balance between government initiatives and burgeoning private sector contributions offers a nuanced picture of this evolving domain.
The policy directions taken by Trump’s administration have not been without controversy, creating a complex dynamic among stakeholders in the space industry, especially concerning budget allocations and international collaboration. The emergence of innovative companies—ranging from Virgin Galactic to Rocket Lab and Sierra Nevada Corporation—has added pressure to a landscape already intensifying with competition. This comprehensive exploration of Trump’s space policy sheds light on the motivations behind his decisions, assessing their implications for America’s readiness to embrace the cosmos while addressing the challenges presented along the way.
The Vision Behind Trump’s Space Policy
At the core of Donald Trump’s space policy is an ambition that extends well beyond Earth. With his administration focusing on making the United States a leader in space exploration and technology, strategic plans have begun to materialize, directing attention toward the Moon, Mars, and even deeper into the universe. Initiatives such as the Artemis program aim to return humans to the Moon, with plans for further exploration to Mars. This audacious vision necessitates a collaborative effort between government agencies like NASA and private companies, particularly SpaceX, which has been at the forefront of commercial spaceflight.

The Artemis Program: A Bold Step Forward
The Artemis program has garnered substantial attention as a cornerstone of Trump’s ambitious agenda. With a target timeline aiming for a lunar landing by 2024, NASA aims to establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon. The program serves not only as a stepping stone for future Mars exploration but also as a vital part of America’s strategy to lead in space research. Funding and organizational partnerships, including private contractors such as Blue Origin and Lockheed Martin, are essential components of this monumental initiative.
However, critics argue that the ambitious goals set forth by the Trump administration may be unrealistic given the estimated costs and technological challenges. The presence of increased budget scrutiny and competing priorities leads to extensive debates about the sustainability of funding initiatives for space exploration projects. Disputes over the division of responsibilities between public and private sectors reflect the evolving landscape of technology in space endeavors, which shapes the future of the space industry.
A Shift in Leadership and Vision
Trump’s approach towards space policy significantly differs from that of previous administrations, reflecting a unique set of priorities focused heavily on competition with China and Russia. The emphasis on national security has led to the establishment of the Space Force, a new military branch dedicated to safeguarding U.S. interests in outer space. This directive showcases the heightened importance placed on military operations within the context of national security, but at what cost to civil space exploration?
Thus, the role of NASA has evolved considerably, transitioning from a primary exploration entity to one that must now strategically collaborate with emerging private entities. The ability of NASA to effectively navigate these changes while maintaining its mission has become more critical than ever. As funding battles persist, Northrop Grumman and other private contractors are vying for NASA contracts, striving to prove essential for the success of upcoming missions.
The Role of Private Industry in Space Exploration
While government agencies like NASA have traditionally led space exploration, Trump’s tenure has marked a shift towards an intensified partnership model that incorporates private enterprises. Companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin are not merely vendors but integral parts of the national agenda for space exploration. The commercial success and innovations these companies bring serve not only to advance technological capabilities but to drive down costs, making space more accessible than ever.
SpaceX: Leading the Charge
SpaceX, led by Elon Musk, has taken significant strides in revitalizing space transportation, demonstrating its capacity through successful launches, reusability of rockets, and ambitious plans for space colonization. Altering the dynamics of both launch contracts and orbital missions, SpaceX continues to be a frontrunner in the commercially-driven space race. NASA partnered with SpaceX for critical missions, tapping into its innovation while reducing dependency on traditional methods.
The implications of SpaceX success extend beyond commercial interests. The collaboration has led to changes in how NASA approaches its respective funding, leading to increased scrutiny regarding budget allocations. Critics claim that focusing resources on companies like SpaceX could undermine public sector research and exploration programs. Nonetheless, advocates argue that such engagements effectively harness the strengths of both sectors to expedite advancements.
The Emergence of Other Players
The rise of new companies such as Rocket Lab and Sierra Nevada Corporation reflects a growing trend in the space industry towards diversification. As these organizations tackle various niches within space exploration—whether small satellite launches or cargo transport to the International Space Station—the increased number of stakeholders changes the competitive dynamic. The incorporation of commercial players not only catalyzes innovation but enhances the agility required to adapt to rapidly changing technologies.
However, this shift has not been without resistance. Challenges arise concerning the allocation of government contracts and concerns over how funds are distributed amongst competing entities. Companies like Boeing have experienced setbacks, leading to questions about the effectiveness of traditional aerospace giants in the new era dominated by innovation and leaner operations.
Funding and Policy Debates
Budget matters are central to Trump’s space policy discussions, highlighting a complex interplay between ambitious plans and fiscal realities. His administration’s proposals for NASA funding display sharp contrasts to previous years, sparking debates on priorities related to space exploration. Notably, Trump’s administration has proposed substantial budget cuts to traditional agencies while advocating for increased support towards private space companies. This shift in funding sources raises questions about the adequacy of government funding for advancing scientific research and exploration.
NASA’s Budget Cuts and Future Implications
Amid the ambitious plans laid out for space exploration, the Trump administration aimed to reduce NASA’s budget by approximately $6 billion, reallocating funds to initiatives aimed at achieving Mars exploration. Such drastic changes raise alarms among researchers who emphasize the importance of sustainable funding for ongoing projects. The emphasis on reallocating resources toward bold initiatives—such as myopic Mars projects—challenges multi-year commitments required for ongoing research, such as climate studies and Earth science programs.
The consequences of reduced funding will undoubtedly ripple through NASA’s capabilities. The potential halting of vital missions has been a point of contention among scientists who warn that vital data and understanding could be put at risk. Issues pertaining to diversity, equity, and inclusion within space agencies may also come to the forefront amid these budget negotiations, creating additional barriers that must be addressed to ensure comprehensive progress.
Public vs. Private Funding Battles
Disputes over public versus private funding expose an evolving power dynamic among stakeholders in the space industry. A tension exists between government priorities and the accelerating pace of technology driven by private companies. Proponents of public funding argue that it is vital for ensuring comprehensive scientific research, while advocates of private funding emphasize commercial viability and rapid advancements that can be achieved with fewer bureaucratic hurdles.
Establishing a balanced approach towards budget allocations remains crucial for maintaining innovation. The presence of multiple avenues for funding—whether through government contracts or private investments—offers a diversified strategy to ensure continued advancements in American space exploration. However, persistent negotiations and adjustments are required to map a path forward that maintains momentum in these ambitious ventures.
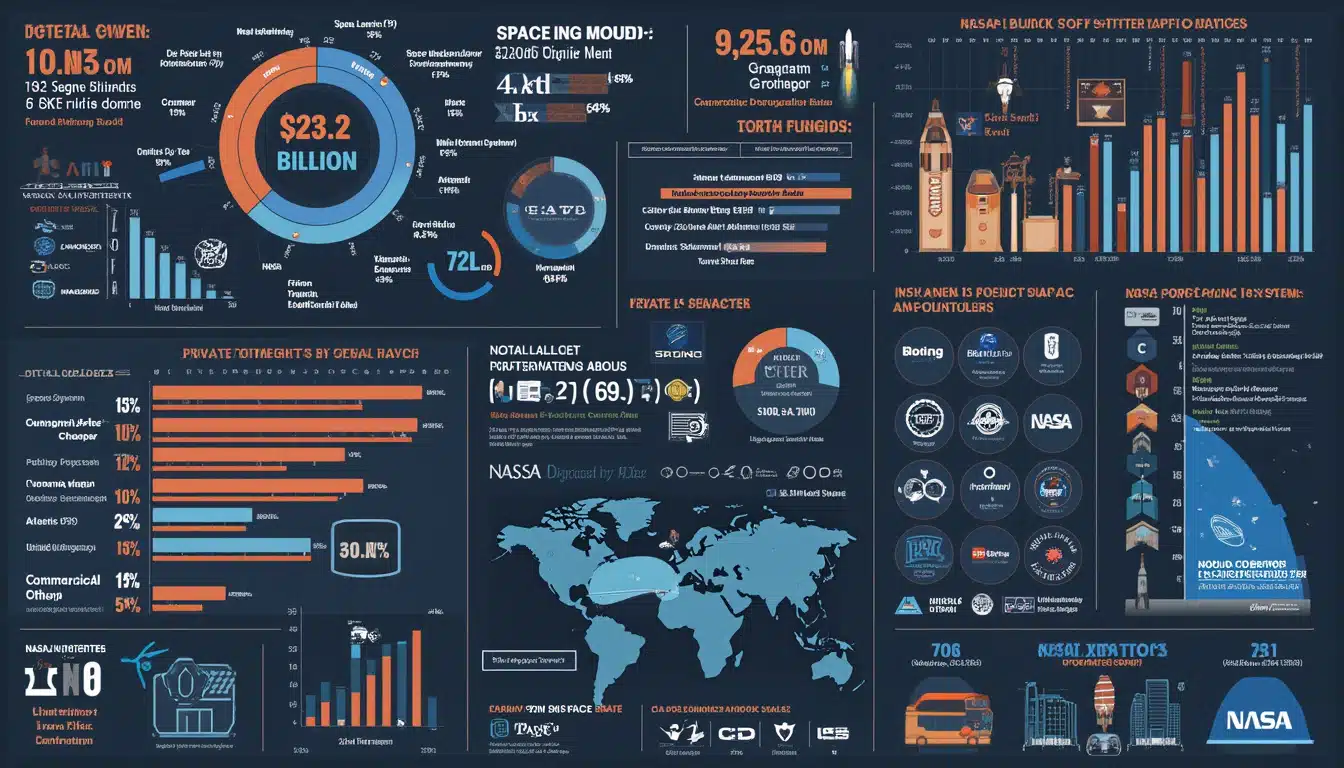
International Collaborations and Space Diplomacy
International partnerships remain an essential theme in shaping effective space policy under Trump’s leadership. Strategic alliances can bolster technological cooperation, enhance resource-sharing and enrich prospects for collaborative missions. A notable focus during this presidency has been on fostering relationships with private sector stakeholders, as well as exploring potential international engagements beyond traditional allies.
The Quest for Global Leadership
Ongoing negotiations with allied nations regarding joint missions to the Moon and Mars highlight a desire for collaborative efforts that offer mutual benefits. Maintaining leadership in space necessitates working with international partners to share knowledge and resources—a challenge complicated by rising tensions with rival powers. The need to manage these relations is crucial to navigate the intricate landscape of global space policy.
Partnership opportunities present themselves through collaborative agreements aimed at enhancing technological development. For instance, the establishment of international coalitions helps facilitate shared investments in emerging technologies and projects, such as those involving next-generation spacecraft and planetary explorations. The ability of U.S. companies like SpaceX to engage with global partners can position them as leaders in the commercial sector of space diplomacy.
Challenges in Diplomacy and Cooperation
Political climates complicate the potential for effective international collaboration in the current landscape. The need for diplomacy remains vital amidst contentious geopolitical situations, particularly with rival nations such as Russia and China vying for dominance in space. Building trust among partners while addressing national interests lays the groundwork for viable space agreements—both politically and commercially. Engaging with international stakeholders can further illuminate avenues for strengthening partnerships within this competitive arena.
Successes and failures in collaboration impact not only individual missions but the overall stability and effectiveness of international policy frameworks. Conclusively, understanding and addressing the challenges posed by international relations will play a critical role in determining the trajectory and viability of future space exploration undertakings.




Leave a Reply